Social Activities
1. Japan Society of Civil Engineers
As the 95th President of the JSCE (2006-2007), Dr. Hamada carried out the following activities.
1-1. Special Presidential Committee Report - The Future of Civil Engineering and The Role of Civil Engineers - March 2007
Special Presidential Committee Report
In this report, the present situation and future prospect surrounding civil engineering, the roles of civil engineers, and the capabilities and qualities required of civil engineers were discussed, and the roles and the strategies of JSCE were shown.
Special Presidential Committee Report ・The Future of Civil Engineering and The Role of Civil Engineers- March 20070

Special Presidential Committee Report
1-2. Joint Proposal on Enhancement of Earthquake Resistance of civil engineering structures and buildings against the long period earthquake ground motions caused by the great earthquakes in the Pacific Ocean
November 2006, Japan Society of Civil Engineers, Architectural Institute of Japan
The maintenance and expansion of the strong-motion seismic network for predicting long-period ground motions caused by earthquakes in the Pacific Ocean is proposed, and the necessity of seismic diagnosis and reinforcement of high-rise buildings is strongly suggested. The report also pointed out the necessity of earthquake-resistant reinforcement of super high-rise buildings, etc. Especially for super high-rise buildings, the long period ground motions were predicted for each region of the country, and recommended that the earthquake resistance should be checked and, if necessary, reinforced. Subsequently, many of Japan's high-rise buildings, such as the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building, were reinforced in accordance with these recommendations.

Joint Proposal by Japan Society by Civil Engineers
1-3. 2000 Presidential Committee Report
The Role of Japan Society by Civil Engineers in Natural Disaster Mitigation - March 2007 In response to the recent increase in the number and severity of natural disasters, this report shows preparedness against future natural disasters, and recommends the role of JSCE for the disaster mitigation in the future.

2000 Presidential Committee Report
1-4. Disseminating the activities of JSCE to the public through the President and the mass media meeting
In order to recover the low level of public recognition of JSCE and civil engineering projects, the president's meetings with media were held periodically to publicize the roles and duties played by JSCE and civil engineers. Many journalists from general newspapers as well as construction industry-related newspapers participated in the conference.
2. Science Council of Japan
As a member of the Science Council of Japan (2005-2011) and the chairperson of the Committee on civil engineering and architecture compiled the following recommendations for academic research in the field of architecture and civil engineering and disseminating their results to the public, and present them to the national government and other relevant organizations in Japan.
2-1. Report "Creation of Safer and More Secure Societies against Globally Increasing Natural Disasters"
The report was submitted to the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, summarizing the elucidation and prediction of natural phenomena that cause disasters, the vulnerability of national land and social structures against disasters, and the role to be played by the Science Council of Japan.

Report of the Science Council of Japan, Building a Safe and Secure Society
2-2. Report "Recreation of Relationships among Humans, Environments and Infrastructures for Establishment of Sustainable Societies"
2-3. Report "International Cooperation for Natural Disaster Reduction"
Japan has been providing support for recovery and reconstruction whenever a natural disaster occurs around the world, but the level of cooperation between Japan and related organizations has been inadequate and their contribution has not been recognized. We recommended that, in the event of a natural disaster overseas, Japan should establish a common information platform among the domestic organizations and even during normal times.

Committee on International Cooperation for Natural Disaster Mitigation, Science Council of Japan
3. Asian Disaster Reduction Center
3-1. The Asian Conference for Disaster Reduction
ADRC is an international organization that consists of 31member countries in Asia, and the central office is located in Kobe, Japan. Asia is the most vulnerable area against natural disasters, more than a half-million people were killed by the disasters during the last half-century. The target of ADRC is to reduce natural disasters in the Asian region through disaster information sharing and exchange of technologies for disaster mitigation among the member countries. For this purpose, ADRC has continued to hold the annual Asian Conference in one of the member countries. The recent meeting was held in Baku, Azerbaijan in 1997, Kobe, Japan in 1998, and Ankara, Turkey in 1999.

Asian Disaster Reduction Center
4. Engineers without Borders, Japan
The Engineers without Borders, Japan (EWBJ) is one of the non-profit organizations which was founded after the 2004 the Indian Ocean Tsunami disaster, and one of the national branches of the Engineering Borders, International. The organization has continued disaster mitigation education and training for elementary school students and junior high school pupils in the Asian countries. On the other hand, it is dispatching senior engineers to Ofunato and Rikuzentokoda cities for the support and assistance for the recovery from the 2011 Great East Japan tsunami disasters. It has also continued to financially as well as technical support the student organizations for disaster mitigation of Waseda University and Kyoto Universities.

Disaster Preparedness Education by Engineers Without Borders
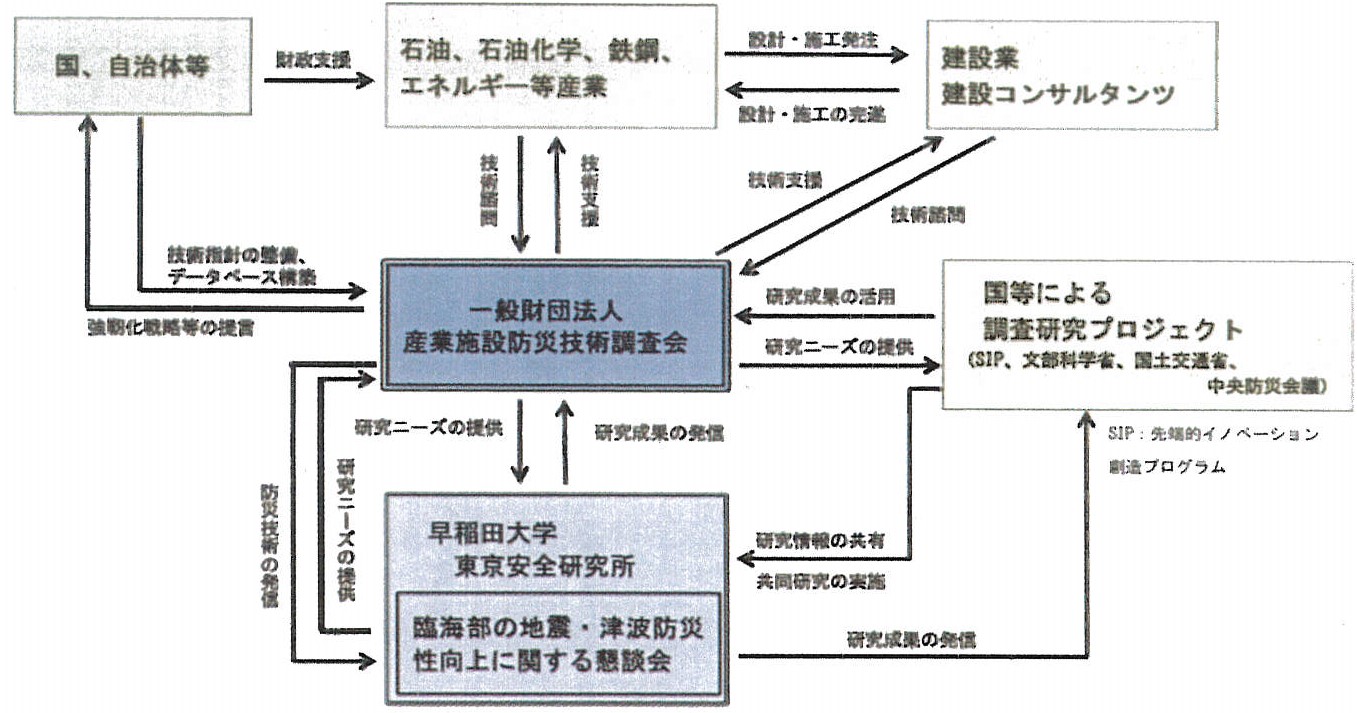
5. Institute for Disaster Reduction of Industrial Complexes
The Institute for Disaster Reduction of Industrial Complexes was established after the Great East Japan Earthquake of 2011, which caused severe damage to industrial facilities in the coastal area. Critical Japanese industries (electricity, gas, oil, petrochemicals, steel, etc.) are located in close proximity to major metropolitan areas such as Tokyo Bay, Ise Bay and Osaka Bay. Most of them are built on artificial lands reclaimed from the bay, and have been severely damaged by liquefaction and strong earthquake ground motions in the past earthquakes. Guidelines for earthquake and tsunami risk assessment and reinforcement methods for industrial facilities have been developed and published. In addition, a consortium with Shinozaki Research Institute, has been formed to manage the "Project for Strengthening the Oil Supply Structure" by the Natural Energy Agency of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.
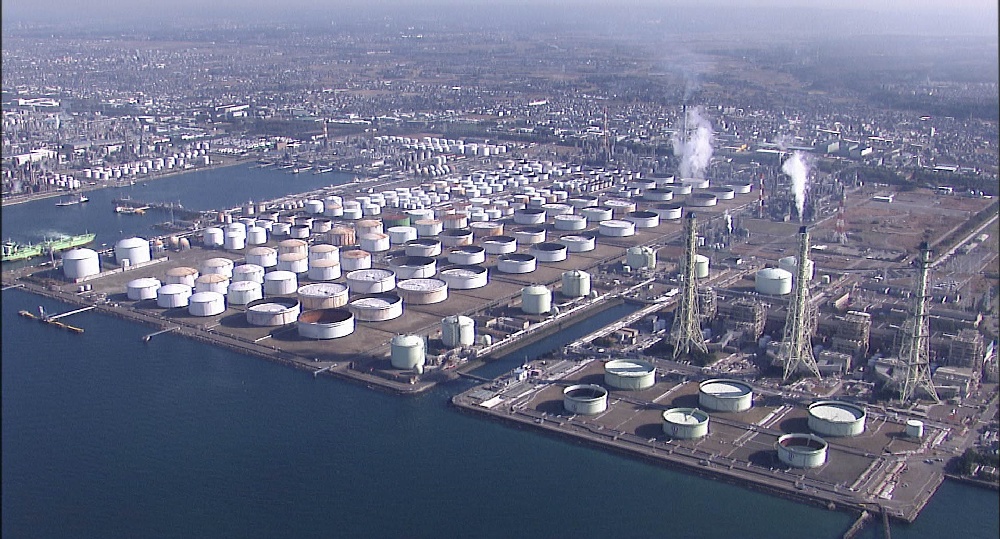

Industrial complexes in the Tokyo Bay area
6. Institute for the Development on filling-up Technology of Abandoned Mines
There are many abandoned coal mines and waste caverns throughout our country. These cavities have often collapsed due to earthquakes and long-term degradation, causing damage to the region. In particular, abandoned lignite mines in the central region of Japan have repeatedly collapsed and suffered local communities.
The Association for the Development of Filling-up Technology has been developing methods to search the existence of underground cavities, cavity filling techniques, and post-filling inspection techniques. These technologies are being used in cavity filling projects. Though technical supports have been provided by the Institute to Mitake Town in Gifu Prefecture its cavity filling project. In Mitake Town, filling work has been continuously carried out with funds from the Japanese government.

Abandoned lignite mines in Mitake Town, Gifu Prefecture
7. Activities at the Sewerage Association of Japan
Sewerage facilities, especially water treatment plants, pumping stations, and other base facilities built near the coast, were severely damaged by the 2011 Tohoku Pacific Earthquake. As the chairman of the "Special Committee on Earthquake Resistance Measures for Sewerage Facilities" organized by the Japan Sewerage Works Association, the damage to sewerage facilities on the Pacific coast of the Tohoku region was investigated in detail, and the design of seismic resistance of sewerage facilities and countermeasures were compiled as "Guidelines and Commentary for Seismic Measures for Sewerage Facilities". The guideline is the first national guideline for the design and countermeasure against tsunamis among the lifeline facilities.

Technical guidelines of Sewage System against Earthquake and Tsunamis
8. Activities at the Tokyo Safety Research Institute, Waseda University
The Tokyo Safety Research Institute, Waseda University, was established in 2014, organized study groups on the improvement of earthquake and tsunami disaster preparedness in the coastal areas. About 50 participants from governmental organizations, academia and the private sectors participated in the conference and discussed technical and social issues, as well as measures taken by the government and local governments to improve the disaster resistance of the waterfront area.
Institute for the Disaster Prevention of the Metropolitan Tokyo
9. Activities at the Reactor Safety Review Board, Nuclear Safety Commission, Science and Technology Agency of the Japanese Government
The National Committee for Nuclear Reactor Safety was in charge of the safety review of geotechnical and civil engineering structures for the seismic safety of newly constructed nuclear power plants. The safety of the ground and facilities at Chubu Electric Power Company, Chugoku Electric Power Company, Tohoku Electric Power Company and others was examined.
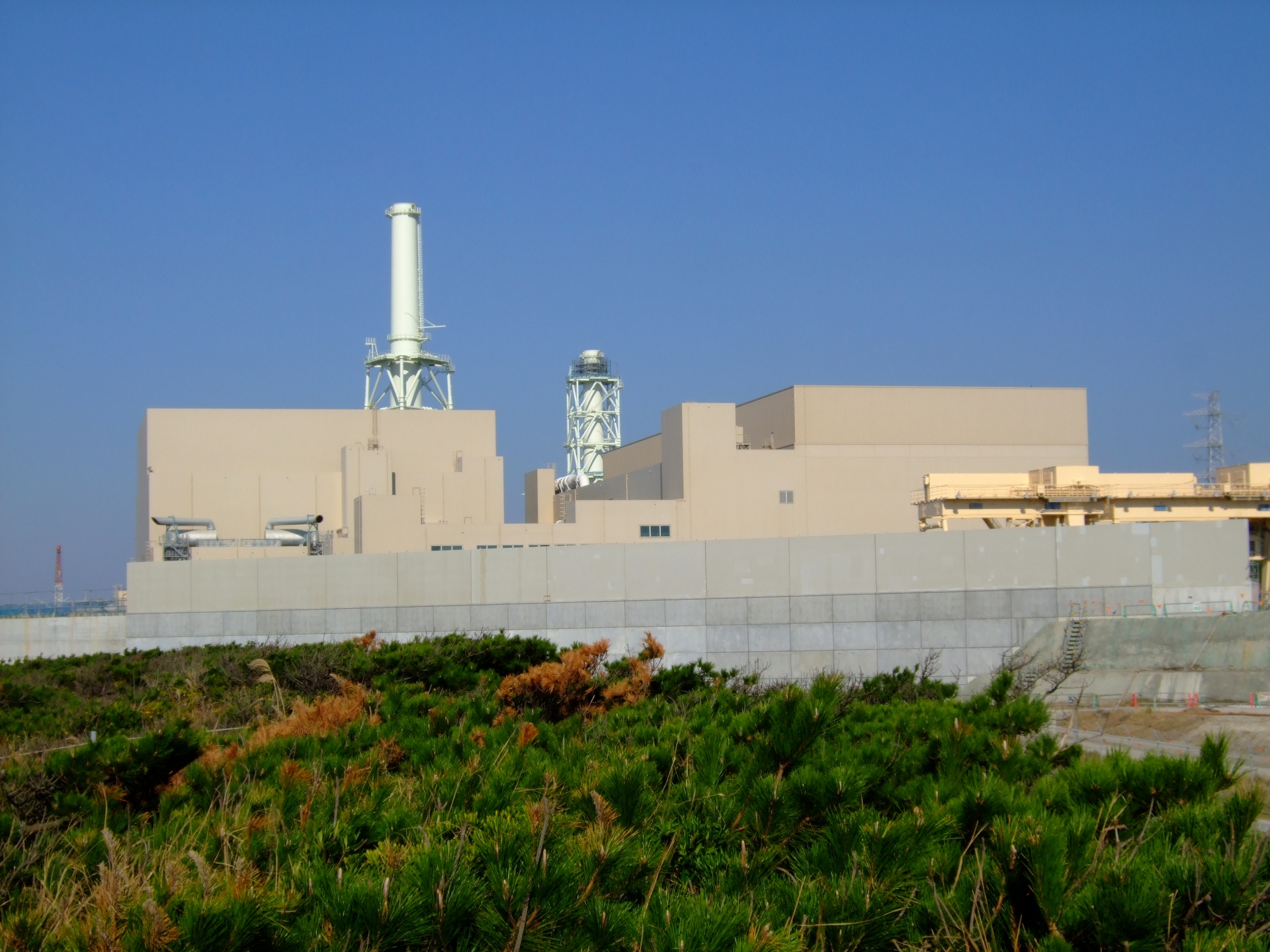

Chubu Electric Power Company's Hamaoka Nuclear Power Station, which was in charge of the safety review